Quantum Simulation
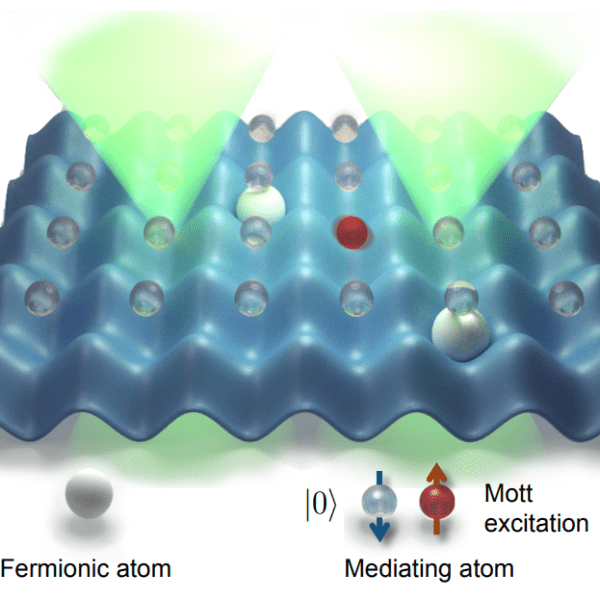
Quantum simulators are setups which are designed to mimic the interactions and dynamics of other relevant many-body systems whose behaviour is very difficult to understand with current numerical methods. When such interactions are obtained in a continuous and global way, one talks about analog quantum simulators, which are generally more resilient to noise and easier…
Quantum and Quantum-Inspired Algorithms
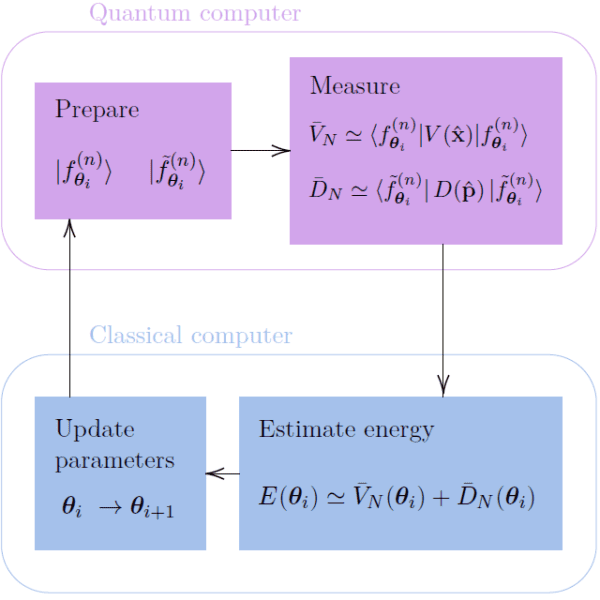
Quantum algorithms take advantage of quantum phenomena such as entanglement and superposition to solve problems unreachable by classical computers, or to outperform them in the performance of similar tasks. While the applications of quantum computing are wide reaching, we are still in the NISQ era, where noise and small numbers of qubits dominate our quantum…
Quantum Optics and Photonics
Quantum optics studies the interaction of light and matter at their most fundamental level (single or few quanta). Apart from its fundamental interest, such interaction is instrumental for several quantum technologies such as sending quantum information between different nodes, measuring systems beyond the limits imposed by classical physics, or inducing quantum gates for quantum computing…
Quantum Computing Hardware
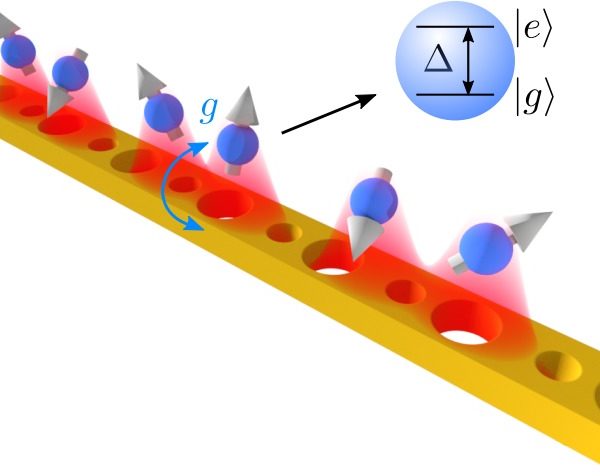
All quantum computation schemes (quantum simulation, quantum annealing, adiabatic quantum computing, gate-based quantum computing…) need an appropriate platform of coherent physical qubits with large anharmonicities and strong tunable coupling between them in order to be realised. A great number of candidates for the physical implementation of quantum computers have been suggested throughout the years, such…